Learning Content In The 2020s: What The Literature Says
March 22nd, 2021
Looking at recent thought leadership in the L&D space, one glaring theme pops out—learning tech. Learning leaders, practitioners, and vendors alike are talking about skills tech, AR / VR, microlearning tech—you’d be forgiven for thinking, “It’s all about tech!” Our recent research confirms the ascendancy of learning tech.1
BUT.
Even as learning tech has its time in the spotlight, learning leaders are realizing that what they’re trying to share via tech—the information that helps employees develop—is equally if not more essential than the tech that delivers it. In short:
The effectiveness of learning tech relies on the strength of the learning content it conveys.
This brings us to our current line of research—content.
In recent years, we’ve seen a massive increase in the amount and types of learning content available to employees—both internally created and owned by the org (proprietary) and externally created (nonproprietary). With this expansion of options, L&D leaders are pressed to ask questions like:
- Where should we get content? Should we create it in-house or acquire it from a third party?
- Should the type of content (i.e., nonproprietary vs. proprietary) change how we deliver learning?
- How can we avoid overwhelming employees with learning content?
- Within my org, who should own what content?
- How can we measure and improve the effectiveness of content?
These questions gave rise to the overarching research question we hope to answer through this work:
How can orgs enable employees to access the right learning content, at the right time, in the right format (to give them the right learning experience)?
Themes from the Literature
We reviewed the current literature on content (including content management, strategy, operations, and tech) to understand what orgs and thought leaders are saying about content. We also wanted to see if any key steps exist to deciphering how orgs think—and should think—about content.
The following word cloud is the product of the 50 articles that we reviewed (see Figure 1).

Figure 1: Learning Content Lit Review Word Cloud | Source: RedThread Research, 2021.
This word cloud illuminates several content-related trends.
- First, Figure 1 highlights the significance of the word “more.” With an ocean of learning content available to employees now, people are overwhelmed. This reality was eloquently described by one author who said:
eLearning content is being created and shared faster than you can blink. While today's employees want to direct their own learning, digital information overload can make that a difficult task without a roadmap.2
This content overload gives rise to the question:
With so much learning content available, how can employees easily find what they really need?
- The prominence of the word “need” in Figure 1 emphasizes the importance of enabling learning at the right time and place. For employees to learn in the flow of work, content must be easily accessible at the point of need.
- Finally, “strategy” in Figure 1 is noticeably smaller than some of the other terms. This reflects a trend we see in the literature: Content strategy is present but isn’t a fully developed concept with L&D quite yet. By contrast, it is a fully developed concept with marketing and enterprise content management—and we drew on some of the literature from these areas for this lit review.
To add to this analysis, the literature reflects 5 key themes:
- Content management tech doesn’t equate to a content strategy
- Marketing and enterprise content management offer lessons about content for L&D
- Democratizing content creation
- Should delivery modality dictate content decisions?
- Current literature says little about proprietary vs. nonproprietary content
Let’s dig deeper.
Content management tech doesn’t equate to a content strategy
Although many L&D articles reference content (CMSs) and learning content management systems (LCMSs), few address how to build a content strategy.
So what exactly is a content strategy? Author Chad Udell writes:
In its simplest terms, content strategy for formal learning is a holistic plan for content—the knowledge that you want the learner to receive and retain.3
A content strategy helps orgs be more intentional about the content learning leaders produce or acquire—typically to support the org’s business goals. It also helps keep content consistent and focused (including a consistent tone and voice—a form a branding). This focus stands in stark contrast to many orgs’ tendency to pump out more and more new learning content for the sake of content, ultimately overwhelming and misguiding employees.4
Hoping to make content more manageable and accessible for employees, some L&D orgs look to content management tech as the “silver bullet” answer—thinking their problems will be solved even if they implement the tech without a clear content strategy. This attempt often backfires—or at least dies a slow, quiet death—when nobody uses the tech.
So, instead of a tech-first approach, learning leaders must design a holistic plan for content—a content strategy—and set up any content management tech to support those larger goals.
A learning content strategy is not the same thing as a learning tech strategy: It’s not enough to buy new tech—orgs need to choose content to support their business and learning goals.
Marketing and enterprise content management offer lessons about content for L&D
Marketing offers relevant advice to the L&D world when thinking through questions related to content. If you swap “buyer” for “learner,” marketing-related resources can share key lessons for L&D on cultivating a consistent brand, conducting a needs analysis, and understanding one’s own audience when it comes to content.5 Both marketers and L&D practitioners need to understand:
- Who their audience is
- Why that audience needs our services
- What content we should provide
- When to trigger the buyer / learner to action
- Where buying / learning can best happen
Marketing offers relevant advice to the L&D world when thinking through questions related to content.
These ideas are captured well in Figure 2.
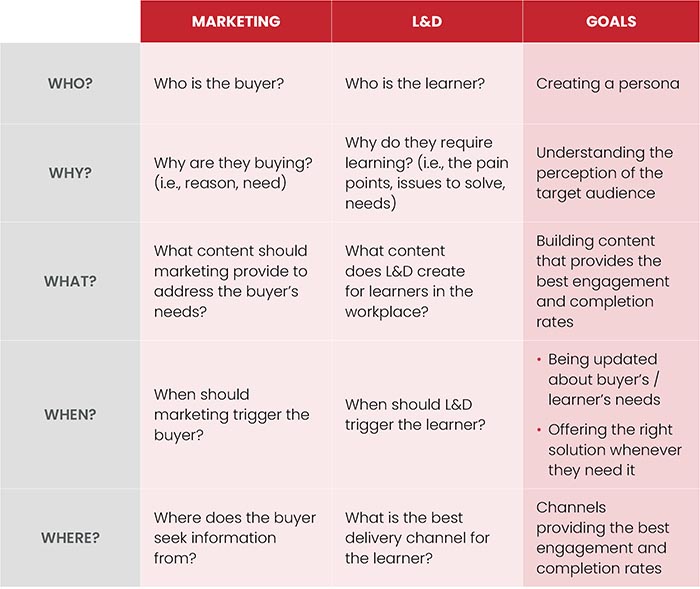
The 5Ws for Content Marketing & L&D | Medium.com, 2018.
Where marketing diverges from L&D is on the point of content ownership. While marketing typically has a central content team and a consolidated source of content operations, many orgs can’t centralize all learning content creation.6 L&D must figure out questions about learning content ownership without leaning on marketers’ experiences.
Where marketing offers insights into understanding our audience and cultivating a brand, enterprise content management focuses on standardization, governance, and modularity to enable orgs to create (or facilitate the creation of), manage, and personalize content at scale. Potential lessons for L&D from this area of the literature include:
- Personalization of content can only be scaled by standardizing content7
- Standardizing content requires breaking it into small, reusable component parts8
- Establishing clear processes for content creation and ownership—governance—is critical to successful content management9
Democratizing content creation
Content has traditionally been handled with a “top-down” methodology, with orgs deciding what employees need to learn, and then creating or providing the relevant content. However, approaches like user-generated content flip this traditional approach on its head. Now employees are encouraged to create learning content.
User-generated content taps into the idea that workers are already sharing information with their peers. One study found that this type of peer-sharing often occurs through answering questions via message or social network (39% of respondents), and through sharing articles, podcasts, and other mediums (37% of respondents).10 The thinking is:
Workers naturally share information with peers, so why not equip them to create content on behalf of the org?11
By actively engaging employees in the process of content creation, user-generated content also promotes learner engagement and satisfaction. The content also tends to be more relevant as it results from real employee needs and experiences.
However, user-generated content isn’t all sunshine and rainbows. While democratized content is proprietary, it’s also less centrally controllable than other proprietary content—bringing in questions about the quality and reliability of the content itself.12 Learning leaders need to ask questions about their role in user-generated content: How should L&D facilitate peer-sharing learning and / or conduct quality reviews of this type of content?
Should delivery dictate content?
Nobody knows—yet.
Different types of delivery options have become increasingly popular of late. Among these are microlearning, mobile learning, and VR: In fact, one recent study documented a 7% increase in mobile learning from 2019 to 2020.13 While the literature reflects this shift, many recent articles discuss how to best create content specific to delivery modalities.
The literature reflects a shift in the learning tech market toward specialized delivery methods—and offers lots of advice about how to create content specific to those methods.
One author, Dr. RK Prasad, offers insight into what a content strategy specific to microlearning could look like. He recommends that learning leaders should rely on gamification more than instructor-led training (ILT): This, he argues, would make learning content more digestible for employees and less expensive for orgs in the long term.14
Another article focused on how to create a content strategy for mobile learning, stressing the importance of the content “lifecycle” and the need to transform content to fit a mobile platform.15 Similarly, another source addressed content development for VR training, and detailed the 6 steps needed to convert content for VR and then test it via this medium.16
The question then becomes:
Should the delivery method change the nature of the content or should orgs make all content reusable, regardless of the original platform?
We couldn’t find any answers in the literature, so we plan to explore this question further in our research.
Current literature says little about proprietary vs nonproprietary content
Heading into this research, we hypothesized that the type of content (i.e., proprietary or nonproprietary) would change how orgs select, prioritize, deliver, and measure learning content.
One reason we believe the content type matters so much is that ownership of the content can change depending on the content type.
In many orgs, a central L&D team fully owns nonproprietary content related to topics like leadership development, while subject-matter experts (SMEs) outside of L&D own proprietary content related to org-specific intellectual property, systems, and processes. L&D may facilitate delivery of that content, but an SME is responsible for creating and maintaining it. User-generated content complicates matters further by distributing creation and ownership even more broadly thoughout the org.
This reality has serious consequences for content strategy, delivery, and measurement. So, for L&D, this means fully answering the question:
Who owns what learning content within the org?
- Should business SMEs be responsible for generating subject-specific content (e.g., related to processes, systems, intellectual property, etc.)?
- Should L&D own all content creation? Should L&D own any content creation?
- How does L&D’s role shift as it relates to both types of content (proprietary and nonproprietary)?
Unfortunately, we found little to no information in the literature weighing in on these questions. We look forward to exploring them in more depth as part of this research.
Top Sources Worth Reading
5 articles in the literature provided great insight into how learning leaders should be thinking of content, including taking advice from some marketing professionals. We found these sources helpful and encourage you to check them out:
10 Steps to Building a Successful Content Strategy
James A. Martin | CMS Wire, January 2018
The article, while initially created for marketing, outlines 10 key steps to creating a content strategy, including choosing the best tech and tailoring the right content for the job.
“To be successful, though, you can’t push out content ‘spray and pray’ style, hoping at least one piece hits its target audience in just the right way.”
Highlights:
- Choose the right tech that allows you to update content
- Be intentional about your target audience and build learner personas
- Conducting a content audit will increase engagement
- Cluster content into digestible chunks for employees
A Content Strategy Isn’t Just for Marketers
Bianca Baumann | Training Industry, Sept/Oct 2017
This article points out the steps L&D can take when creating and implementing a content strategy, pulling from parallels with marketing.
“Ultimately, having a strategy in place helps create meaningful, engaging and sustainable content, and allows to identify the right content at the right time for the right audience.”
Highlights:
- Leaders need to think through both the substance and structure of the content
- Leaders should consider workflow (e.g., resources needed) and governance (e.g., policies, decision-makers)
- Implementing a content strategy requires the following steps (resembling the ADDIE17 model):
- First, learning leaders need to identify a training gap (analysis), strategize before designing (strategy), and create a communication program upfront (plan)
- Next, leaders need to consider reusing content in different forms (create) and think through different learning modalities (deliver)
- Finally, leaders need to align measures with their org’s needs and objectives (measure) and make sure to keep content updated (maintain)
Reusing Content Is Key in Today's Quickly Changing Marketing Landscape
Anjali Yakkundi | CMS Wire, November 2020
This piece discusses how content can be reused by considering content assets to be more like Lego pieces than fixed creations, in order to adapt content to different delivery platforms. This Lego approach frees content creators from spending time updating, managing, and tailoring content—freeing them to focus on other activities like content strategy.
“By breaking down content to smaller, reusable chunks, marketing teams can more easily reuse, recombine and repurpose content to be used on multiple channels.”
Highlights:
- To democratize the learning, content owners should reuse the content and involve multiple team members in the process
- Content owners need to act with agility: They can use a “test-and-iterate" content strategy and be ready to shift priorities when required
- When repurposing content, it’s important to make any changes needed for the context in which the learning’s being presented to the target audience
Bringing Content Strategy into the Blend
Phylise Banner | TD Magazine, August 2017
This magazine article discusses how blended learning can be best served with a content strategy that addresses 3 domains: objective, content, and human.
“When content strategy is done well, no one notices that it’s there. They are too engaged with the experience—which is exactly what we want from our learners.”
Highlights:
- Content strategists need to:
- Create learner personas to describe and understand the attributes of employees
- Build an org-readiness matrix
- Conduct a content audit to analyze which types of content are working
- Understand workflow and governance by having a content lifecycle
- Identify a team to facilitate the learning culture and carry out the content strategy
User-Generated Content: Socialization of eLearning content
Satyabrata Das | eLearning Industry, December 2020.
This article lays out key advantages and disadvantages of user-generated content and the reasons why this type of content’s becoming increasingly popular.
Highlights:
- User-generated content’s gaining traction in formal learning (while it’s been popular in informal learning)
- Advantages of user-generated content include high engagement, greater relevance, and greater acceptability
- Disadvantages of user-generated content include dependency on a few users to generate content, questionable reliability and accuracy of the content, and incomplete coverage of relevant areas
Additional Reading Recommendations
- “Tip: Content Strategy for Continuous Learning,” Learning Solutions / Monica Kraft, 2014.
- "Delivering Personalized Experiences at Scale: Three Kinds of Output Types," Content Rules / Val Swisher, 2020.
- “Transforming L&D Content Into Immersive VR Training Tools,” eLearning Industry / Christopher Pappas, 2020.
- “Microlearning Content Strategy ROI: How To Maximize It With Gamification,” eLearning Industry / RK Prasad, 2020.
- “Engaging Learners Today: Five Key Takeaways from Content Marketing,”com / Vibons, 2018.
- “Why You Should Rethink Your Learning Content Management Strategy,” Cornerstone OnDemand, 2018.
Heather Gilmartin Adams
Footnotes
- The Learning Tech Landscape: More, Just More, RedThread Research / Dani Johnson, 2020.
- “Why you should rethink your learning content management strategy,” Cornerstone OnDemand, February 2018.
- “How to Create a Content Strategy for Mobile Learning,” ATD / Chad Udell, July 2014.
- “Content Factors for 2021: What You Need To Know,” Content Science Review, January 2021.
- Engaging Learners Today: Five Key Takeaways from Content Marketing, Vibons / Medium 2018.
- How To Build a Content Operation, Content Science Review, 2021.
- “The Personalization Paradox: Why Companies Fail at Personalization,” Content Rules / Val Swisher, 2020.
- Ibid.
- “Strategy Matters: Content 2.0,” Performance Matters Podcast / Conrad Gottfredson and Bob Mosher, 2021.
- “How the Workforce Learns: User-Generated Content,” Todd Tauber / Degreed, 2019.
- Ibid.
- “User-Generated Content: Socialization of eLearning Content,” Satyabrata Das / eLearning Industry, 2020.
- A review of L&D budget allocations in 2020, Rocco Brudno / Coassemble, 2020.
- “5 Ways Gamification Maximizes The Microlearning Content Strategy ROI,” eLearning Industry / RK Prasad, September 2020.
- “How to Create a Content Strategy for Mobile Learning,” ATD / Chad Udell, July 2014.
- “Transforming L&D Content Into Immersive VR Training Tools: A 6-Step Guide,” eLearning Industry / Christopher Pappas, July 2020.
- “ADDIE” is an acronym—analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation—for a 5-stage development process that’s performed in this order, with a focus on reflection and iteration.